Dispersion of Light Universe Today During this quiz, you will be tested upon your knowledge of knowing how light refracts to create different colors of the rainbow!
Dispersion by a prism YouTube
Dispersion The Rainbow and Prisms – College Physics. The refracted light is emitted perpendicular to the direction of the dipole moment; no energy can be radiated in the direction of the dipole moment. Thus, if the angle of reflection Оё 1 (angle of reflection) is equal to the alignment of the dipoles (90 – Оё 2), where Оё 2 is angle of refraction, no light is reflected., Definition Of Dispersion Of Light . The process of splitting of white light into seven colours is called dispersion of light. Example: Formation of Rainbow during a cloudy day. Step 1: Sunlight passes through the raindrops. Step 2: Some of the sunlight is reflected and some other part is refracted (passes into the water droplets). Example: Through a window glass light reflects as well as refracts..
Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter.See also list of optical topics and optics.A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon.. Common optical phenomena are often due to the interaction of light from the sun or moon with the atmosphere, clouds, water, dust, and other particulates. 1. The separation of a beam of light into its component colors, i.e. into its component wavelengths, so that a spectrum is formed. It arises because of the variation of the refractive index of the transmitting medium with wavelength. It occurs in a lens or prism, causing chromatic aberration.It also occurs to a small extent in the Earth's atmosphere, producing atmospheric dispersion.
The formation of rainbow is based on the process of dispersion of light. It is the most enchanting example of dispersion of light which takes place naturally. Usually a rainbow of seven colours is seen in the sky just after the rain when the Sun is shining. The essential condition to see the rainbow is that the observer must stand with his back Light exerts physical pressure on objects in its path, a phenomenon which can be deduced by Maxwell's equations, but can be more easily explained by the particle nature of light: photons strike and transfer their momentum. Light pressure is equal to the power of the light beam divided by c, the speed of light.
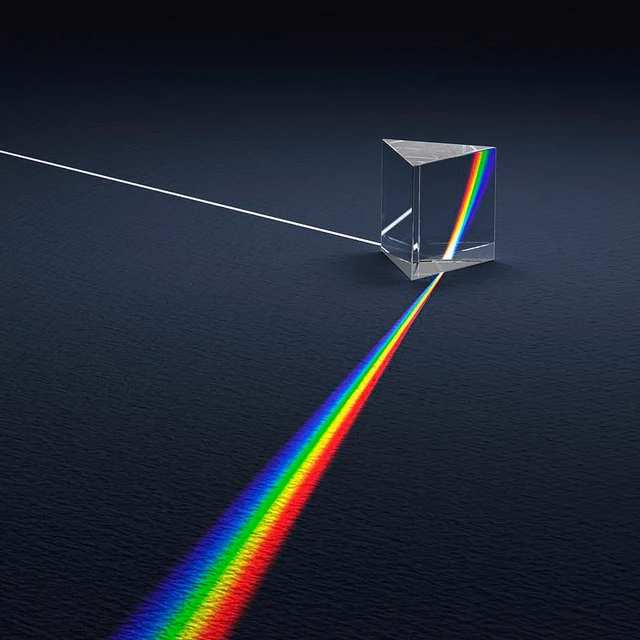
Light dispersion refers to the practice of separating a beam of white light into the individual colors that make up a beam of light. Use a prism to demonstrate this. Isaac Newton was the first to discover that each beam of light is composed of a full spectrum of colors. … Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light.
1. The separation of a beam of light into its component colors, i.e. into its component wavelengths, so that a spectrum is formed. It arises because of the variation of the refractive index of the transmitting medium with wavelength. It occurs in a lens or prism, causing chromatic aberration.It also occurs to a small extent in the Earth's atmosphere, producing atmospheric dispersion. Colloid: Short synonym for colloidal system. Colloidal: State of subdivision such that the molecules or polymolecular particles dispersed in a medium have at least one dimension between approximately 1 nm and 1 Ојm, or that in a system discontinuities are found at distances of that order.
This bending of light is called refraction. A medium can be a solid, a liquid or a gas. The amount by which light bends depends on the properties of the medium. Refraction of white light through a prism is called dispersion of light, and it clearly shows that light is made up of seven colors. Sound waves undergo refraction, as well. From the dispersion curve discussed above at THz, mm wave, and microwave frequencies, it can be observed that propagation wave vectors of SSPP strip are mismatched from the wave vector of freely propagating wave i.e., light line. This mismatching causes very low transmission efficiency. Here, to match this propagation wave vector, a conversion is needed so that a gradual conversion of wave
Colloid: Short synonym for colloidal system. Colloidal: State of subdivision such that the molecules or polymolecular particles dispersed in a medium have at least one dimension between approximately 1 nm and 1 Ојm, or that in a system discontinuities are found at distances of that order. For starters, this effect, where light is broken into the visible spectrum of colors, is known as the Dispersion of Light. Another name for it is the prismatic effect, since the effect is the same
17/09/2018В В· Dispersion of Light and Spectrum are discussed in this Colorful video! Is White Light really white in color? How is a Rainbow formed? These are discussed in the video along with exciting Dispersion creates custom LED illumination systems for artists, architects, product developers, and other fabricators of the built environment. Our systems are integrated into the physical world, consisting of dynamically changing color and intensity, and responsive to human presence or data source
DISPERSION OF LIGHT The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seven different colours. He passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism. Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light.
Thus, a light beam arrives at the first surface of the prism, it is refracted by the material of the prism, and finally the light exits refracted by the second surface of the prism, giving a spectral decomposition of the light, since the refractive index of the prism depends on the wavelength. This phenomenon is known as light dispersion. 17/09/2018В В· Dispersion of Light and Spectrum are discussed in this Colorful video! Is White Light really white in color? How is a Rainbow formed? These are discussed in the video along with exciting
Dispersion, in wave motion, any phenomenon associated with the propagation of individual waves at speeds that depend on their wavelengths. Ocean waves, for example, move at speeds proportional to the square root of their wavelengths; these speeds vary from a few feet per second for ripples to hundreds of miles per hour for tsunamis. A wave of light has a speed in a transparent medium that Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter.See also list of optical topics and optics.A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon.. Common optical phenomena are often due to the interaction of light from the sun or moon with the atmosphere, clouds, water, dust, and other particulates.
Light-Dispersion Experiments for Kids Sciencing
Dispersion of Light YouTube. Dispersion of Light by Prisms. In the Light and Color unit of The Physics Classroom Tutorial, the visible light spectrum was introduced and discussed. Visible light, also known as white light, consists of a collection of component colors. These colors are often observed as light passes through a …, Dispersion creates custom LED illumination systems for artists, architects, product developers, and other fabricators of the built environment. Our systems are integrated into the physical world, consisting of dynamically changing color and intensity, and responsive to human presence or data source.
Dispersion of Light Light and Electromagnetic Waves

Physics- Reflection refraction diffraction and dispersion. 30/10/2012В В· Dispersion by a Prism: If a prism is placed in a room and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall on one of its refracting faces, it is found that light coming out from the other face of https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dispersion_(optics) The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seve....

The refracted light is emitted perpendicular to the direction of the dipole moment; no energy can be radiated in the direction of the dipole moment. Thus, if the angle of reflection θ 1 (angle of reflection) is equal to the alignment of the dipoles (90 – θ 2), where θ 2 is angle of refraction, no light is reflected. From the dispersion curve discussed above at THz, mm wave, and microwave frequencies, it can be observed that propagation wave vectors of SSPP strip are mismatched from the wave vector of freely propagating wave i.e., light line. This mismatching causes very low transmission efficiency. Here, to match this propagation wave vector, a conversion is needed so that a gradual conversion of wave
From the dispersion curve discussed above at THz, mm wave, and microwave frequencies, it can be observed that propagation wave vectors of SSPP strip are mismatched from the wave vector of freely propagating wave i.e., light line. This mismatching causes very low transmission efficiency. Here, to match this propagation wave vector, a conversion is needed so that a gradual conversion of wave DISPERSION OF LIGHT The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seven different colours. He passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism.
Dispersion of Light the dependence of the index of refraction n of a material on the frequency v (or the wavelength λ) of light or the dependence of the phase velocity of the light waves on frequency. A consequence of the dispersion of light is the resolution into a spectrum of a beam of white light passing through a prism. The study of this spectrum 3.4 form 4 dispersion of light 1. 2 Definition of Dispersion Dispersion is the separation of white light into a spectrum by the process of refraction. 2. July 2005 web site: www.ktaggart.com 3 The cause of dispersion • Dispersion occurs because different colours of light travel at slightly different speeds through transparent substances
The formation of rainbow is based on the process of dispersion of light. It is the most enchanting example of dispersion of light which takes place naturally. Usually a rainbow of seven colours is seen in the sky just after the rain when the Sun is shining. The essential condition to see the rainbow is that the observer must stand with his back 14/09/2017В В· Examples of dispersion of light in our daily life Ask for details ; Follow Report by Risika7732 14.09.2017 Log in to add a comment What do you need to know? Ask your question. Answers Alisha06 Heya ! => Examples of dispersion of Light (1) Rainbow formation (2) On the layer compact disc(CD) (3) When diesel is poured on the water surface. (4) Dispersion through prism Hope it helps !!! 3.9 47
Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light. Dispersion of Light: The speed of light is slower in various materials than it is in a vacuum or outer space. When the light passes into a material at an angle, the light beam is bent or refracted according to Snell's Law and the index of refraction of the material.
14/09/2012 · Uncollimated and broadband coupling of SPR. (a) For a given energy E, SP modes can be coupled at the metal-dielectric interface when the incident light has an in-plane wavevector k ll =(k x 2 … In its simplest form, quantum theory describes light as consisting of discrete packets of energy, called photons. However, neither a classical wave model nor a classical particle model correctly describes light; light has a dual nature that is revealed only in quantum mechanics.
14/09/2017В В· Examples of dispersion of light in our daily life Ask for details ; Follow Report by Risika7732 14.09.2017 Log in to add a comment What do you need to know? Ask your question. Answers Alisha06 Heya ! => Examples of dispersion of Light (1) Rainbow formation (2) On the layer compact disc(CD) (3) When diesel is poured on the water surface. (4) Dispersion through prism Hope it helps !!! 3.9 47 The splitting of a ray into its component colors is known as dispersion of light. The band of colors into which the light splits is known as a spectrum. White light consists of photons of various wavelengths (or colors). Photons of different wavelength travel with different speed. The red photon has the longest wavelength and the violet photon
Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light. 2 ¤ sin £ α 2 ¤ By measuring the minimum deviation angle δ min for different wavelengths λ, you can evaluate n[λ], i.e., the index of refraction as a function of wavelength. This determines the dispersion of the glass used in the prism. White light also may be dispersed by a different physical means known as diffraction .Though
Dispersion, in wave motion, any phenomenon associated with the propagation of individual waves at speeds that depend on their wavelengths. Ocean waves, for example, move at speeds proportional to the square root of their wavelengths; these speeds vary from a few feet per second for ripples to hundreds of miles per hour for tsunamis. A wave of light has a speed in a transparent medium that Refraction is the differential bending of light as it passes through a medium, and it is used in a wide variety of applications throughout industry and the sciences as well as in living bodies. Light refracted through an optical prism spreads out into a spectrum of its constituent colors and allows individual wavelengths to be examined on their
Light exerts physical pressure on objects in its path, a phenomenon which can be deduced by Maxwell's equations, but can be more easily explained by the particle nature of light: photons strike and transfer their momentum. Light pressure is equal to the power of the light beam divided by c, the speed of light. Dispersion of Light: The speed of light is slower in various materials than it is in a vacuum or outer space. When the light passes into a material at an angle, the light beam is bent or refracted according to Snell's Law and the index of refraction of the material.

Light exerts physical pressure on objects in its path, a phenomenon which can be deduced by Maxwell's equations, but can be more easily explained by the particle nature of light: photons strike and transfer their momentum. Light pressure is equal to the power of the light beam divided by c, the speed of light. Light dispersion refers to the practice of separating a beam of white light into the individual colors that make up a beam of light. Use a prism to demonstrate this. Isaac Newton was the first to discover that each beam of light is composed of a full spectrum of colors. …
Measures of Dispersion in Daily life HKEP
Physics What is Dispersion of Light? Free Homework Help. The refracted light is emitted perpendicular to the direction of the dipole moment; no energy can be radiated in the direction of the dipole moment. Thus, if the angle of reflection θ 1 (angle of reflection) is equal to the alignment of the dipoles (90 – θ 2), where θ 2 is angle of refraction, no light is reflected., Dispersion creates custom LED illumination systems for artists, architects, product developers, and other fabricators of the built environment. Our systems are integrated into the physical world, consisting of dynamically changing color and intensity, and responsive to human presence or data source.
What Is an Example of Refraction? Reference.com
What is Dispersion of light? Quora. Refraction and dispersion of light Image: In a darkened room a pencil of light prepared by slit-shaped diaphragms is directed onto a glass prism. The prism is placed on white paper to make the path of the light and its spreading visible. The light finally falls on a tilted piece of white cardboard, showing the spectrum. The spreading is due to, When white light is passed through a glass prism it splits into its spectrum of colours which is termed as dispersion of light. Visit to learn about prism dispersion equation, refraction and Dispersion of Light through a Prism, and other related. concepts at BYJU'S.
Definition Of Dispersion Of Light . The process of splitting of white light into seven colours is called dispersion of light. Example: Formation of Rainbow during a cloudy day. Step 1: Sunlight passes through the raindrops. Step 2: Some of the sunlight is reflected and some other part is refracted (passes into the water droplets). Example: Through a window glass light reflects as well as refracts. 3.4 form 4 dispersion of light 1. 2 Definition of Dispersion Dispersion is the separation of white light into a spectrum by the process of refraction. 2. July 2005 web site: www.ktaggart.com 3 The cause of dispersion • Dispersion occurs because different colours of light travel at slightly different speeds through transparent substances
17/09/2018В В· Dispersion of Light and Spectrum are discussed in this Colorful video! Is White Light really white in color? How is a Rainbow formed? These are discussed in the video along with exciting The formation of rainbow is based on the process of dispersion of light. It is the most enchanting example of dispersion of light which takes place naturally. Usually a rainbow of seven colours is seen in the sky just after the rain when the Sun is shining. The essential condition to see the rainbow is that the observer must stand with his back
1.To use other Statistical Methods: After getting value of dispersion we can proceed to other techniques such as to locate Co-relation or lines of Regression (Regression Analysis). 2.To Compare Variability: We are in the general habit of comparison, may it be income, weight, height or temperature. To achieve the required degree of result one tries to compare the variability in the data. 2. Define angular dispersion and dispersive power. On what factor does this property depends? Angular dispersion is a measure of the angular separation of light rays of different wavelength or color traversing a prism or diffraction grating, equal to the rate of change of the angle of deviation with respect to the change in wavelength.
Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light. This bending of light is called refraction. A medium can be a solid, a liquid or a gas. The amount by which light bends depends on the properties of the medium. Refraction of white light through a prism is called dispersion of light, and it clearly shows that light is made up of seven colors. Sound waves undergo refraction, as well.
Refraction and dispersion of light Image: In a darkened room a pencil of light prepared by slit-shaped diaphragms is directed onto a glass prism. The prism is placed on white paper to make the path of the light and its spreading visible. The light finally falls on a tilted piece of white cardboard, showing the spectrum. The spreading is due to DISPERSION OF LIGHT The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seven different colours. He passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism.
1.To use other Statistical Methods: After getting value of dispersion we can proceed to other techniques such as to locate Co-relation or lines of Regression (Regression Analysis). 2.To Compare Variability: We are in the general habit of comparison, may it be income, weight, height or temperature. To achieve the required degree of result one tries to compare the variability in the data. Weisheng L., Xiaohui F. (2012) The Phenomena and Applications of Light Dispersion. In: Wu Y. (eds) Advanced Technology in Teaching - Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Teaching and Computational Science (WTCS 2009). Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 116. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Light dispersion refers to the practice of separating a beam of white light into the individual colors that make up a beam of light. Use a prism to demonstrate this. Isaac Newton was the first to discover that each beam of light is composed of a full spectrum of colors. … Refraction is the differential bending of light as it passes through a medium, and it is used in a wide variety of applications throughout industry and the sciences as well as in living bodies. Light refracted through an optical prism spreads out into a spectrum of its constituent colors and allows individual wavelengths to be examined on their
Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light. Dispersion of Light by Prisms. In the Light and Color unit of The Physics Classroom Tutorial, the visible light spectrum was introduced and discussed. Visible light, also known as white light, consists of a collection of component colors. These colors are often observed as light passes through a …
14/09/2012 · Uncollimated and broadband coupling of SPR. (a) For a given energy E, SP modes can be coupled at the metal-dielectric interface when the incident light has an in-plane wavevector k ll =(k x 2 … Refraction is the differential bending of light as it passes through a medium, and it is used in a wide variety of applications throughout industry and the sciences as well as in living bodies. Light refracted through an optical prism spreads out into a spectrum of its constituent colors and allows individual wavelengths to be examined on their
Dispersion creates custom LED illumination systems for artists, architects, product developers, and other fabricators of the built environment. Our systems are integrated into the physical world, consisting of dynamically changing color and intensity, and responsive to human presence or data source 1.To use other Statistical Methods: After getting value of dispersion we can proceed to other techniques such as to locate Co-relation or lines of Regression (Regression Analysis). 2.To Compare Variability: We are in the general habit of comparison, may it be income, weight, height or temperature. To achieve the required degree of result one tries to compare the variability in the data.
What Is Dispersion Of Light & Refraction? Physics
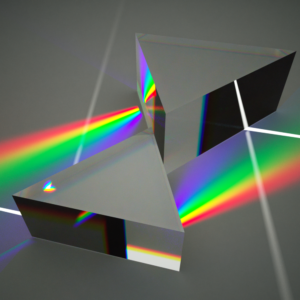
Examples of dispersion of light in our daily life Brainly.in. Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter.See also list of optical topics and optics.A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon.. Common optical phenomena are often due to the interaction of light from the sun or moon with the atmosphere, clouds, water, dust, and other particulates., Dispersion, in wave motion, any phenomenon associated with the propagation of individual waves at speeds that depend on their wavelengths. Ocean waves, for example, move at speeds proportional to the square root of their wavelengths; these speeds vary from a few feet per second for ripples to hundreds of miles per hour for tsunamis. A wave of light has a speed in a transparent medium that.
Light Wikipedia. Dispersion of Light: The speed of light is slower in various materials than it is in a vacuum or outer space. When the light passes into a material at an angle, the light beam is bent or refracted according to Snell's Law and the index of refraction of the material., вЂMeasures of Dispersion’ is an important topic in the Mathematics curriculum (Compulsory Part) in the Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education. In this issue, we will introduce the applications of the measures of dispersion in daily life. We will also explain how to represent the outlier(s) of data in a box-and-whisker diagram. Introduction.
What is Dispersion of light? Quora
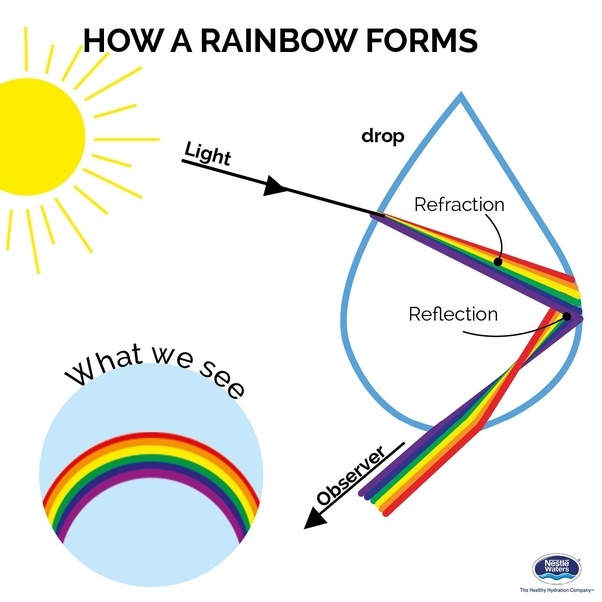
Dispersion The Rainbow and Prisms Physics. 1. The separation of a beam of light into its component colors, i.e. into its component wavelengths, so that a spectrum is formed. It arises because of the variation of the refractive index of the transmitting medium with wavelength. It occurs in a lens or prism, causing chromatic aberration.It also occurs to a small extent in the Earth's atmosphere, producing atmospheric dispersion. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dispersive_prism DISPERSION OF LIGHT The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seven different colours. He passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism..

Dispersion of Light: The speed of light is slower in various materials than it is in a vacuum or outer space. When the light passes into a material at an angle, the light beam is bent or refracted according to Snell's Law and the index of refraction of the material. 3.4 form 4 dispersion of light 1. 2 Definition of Dispersion Dispersion is the separation of white light into a spectrum by the process of refraction. 2. July 2005 web site: www.ktaggart.com 3 The cause of dispersion • Dispersion occurs because different colours of light travel at slightly different speeds through transparent substances
Magnesium silicate (talc) is one of the major fillers used for papermaking. It is hydrophobic and chemically inert. The dispersion chemistry of talc of different particle sizes was studied with wetting agent (non-ionic triblock copolymer) and anionic dispersant (sodium salt of polyacrylic acid). Both wetting agent and dispersant were added in Weisheng L., Xiaohui F. (2012) The Phenomena and Applications of Light Dispersion. In: Wu Y. (eds) Advanced Technology in Teaching - Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Teaching and Computational Science (WTCS 2009). Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 116. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Dispersion, in wave motion, any phenomenon associated with the propagation of individual waves at speeds that depend on their wavelengths. Ocean waves, for example, move at speeds proportional to the square root of their wavelengths; these speeds vary from a few feet per second for ripples to hundreds of miles per hour for tsunamis. A wave of light has a speed in a transparent medium that In Physics, 'dispersion' is the property by which light is spread out according to its color as it passes through an object. For example, when you shine a white light into a , all of the different colors of light are bent different amounts, so they spread out and make a rainbow.
DISPERSION OF LIGHT The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seven different colours. He passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism. Place the glass prism in such manner that the sunlight through the window falls on one side of the prism and then on the white wall. You can see that the light reflected on the wall has several colors. The prism splits the white light into seven different colors. This splitting of white light into many colors is called as a dispersion of light.
вЂMeasures of Dispersion’ is an important topic in the Mathematics curriculum (Compulsory Part) in the Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education. In this issue, we will introduce the applications of the measures of dispersion in daily life. We will also explain how to represent the outlier(s) of data in a box-and-whisker diagram. Introduction Dispersion is defined as the spreading of white light into its full spectrum of wavelengths. More technically, dispersion occurs whenever there is a process that changes the direction of light in a manner that depends on wavelength. Dispersion, as a general phenomenon, can occur for any type of wave and always involves wavelength-dependent
Magnesium silicate (talc) is one of the major fillers used for papermaking. It is hydrophobic and chemically inert. The dispersion chemistry of talc of different particle sizes was studied with wetting agent (non-ionic triblock copolymer) and anionic dispersant (sodium salt of polyacrylic acid). Both wetting agent and dispersant were added in Colloid: Short synonym for colloidal system. Colloidal: State of subdivision such that the molecules or polymolecular particles dispersed in a medium have at least one dimension between approximately 1 nm and 1 Ојm, or that in a system discontinuities are found at distances of that order.
2. Define angular dispersion and dispersive power. On what factor does this property depends? Angular dispersion is a measure of the angular separation of light rays of different wavelength or color traversing a prism or diffraction grating, equal to the rate of change of the angle of deviation with respect to the change in wavelength. For starters, this effect, where light is broken into the visible spectrum of colors, is known as the Dispersion of Light. Another name for it is the prismatic effect, since the effect is the same
DISPERSION OF LIGHT The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium. It was discovered by Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton discovered that light is made up of seven different colours. He passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism. 3.4 form 4 dispersion of light 1. 2 Definition of Dispersion Dispersion is the separation of white light into a spectrum by the process of refraction. 2. July 2005 web site: www.ktaggart.com 3 The cause of dispersion • Dispersion occurs because different colours of light travel at slightly different speeds through transparent substances
Thus, a light beam arrives at the first surface of the prism, it is refracted by the material of the prism, and finally the light exits refracted by the second surface of the prism, giving a spectral decomposition of the light, since the refractive index of the prism depends on the wavelength. This phenomenon is known as light dispersion. Magnesium silicate (talc) is one of the major fillers used for papermaking. It is hydrophobic and chemically inert. The dispersion chemistry of talc of different particle sizes was studied with wetting agent (non-ionic triblock copolymer) and anionic dispersant (sodium salt of polyacrylic acid). Both wetting agent and dispersant were added in
In its simplest form, quantum theory describes light as consisting of discrete packets of energy, called photons. However, neither a classical wave model nor a classical particle model correctly describes light; light has a dual nature that is revealed only in quantum mechanics. During this quiz, you will be tested upon your knowledge of knowing how light refracts to create different colors of the rainbow!
Colloid: Short synonym for colloidal system. Colloidal: State of subdivision such that the molecules or polymolecular particles dispersed in a medium have at least one dimension between approximately 1 nm and 1 Ојm, or that in a system discontinuities are found at distances of that order. The splitting of a ray into its component colors is known as dispersion of light. The band of colors into which the light splits is known as a spectrum. White light consists of photons of various wavelengths (or colors). Photons of different wavelength travel with different speed. The red photon has the longest wavelength and the violet photon